Que : Write a program to check whether there is a loop in linked list . For example see in the following figure we have loop :
Method 1 : ( Brute Force Method)
Brute Force Method is that start with first node and see whether there is any node whose next pointer is current node address . If there is a node with same address then that indicates that some other node is pointing to the the current node and showing there is loop int the linked list . Repeat this process until all the nodes are traversed or checked .
Method 2 : (Hashing )
1) Traverse the linked list nodes one by one and save address of the node in a table .
2) Check if the node address is there in hash table or not .
3) If it is already there in the hash table then that indicates that we are visiting the node which was already visited . This is possible only if the given linked list has a loop in it.
4) If the address of the node is not there in the hash table the insert that node address into the hash table .
5) Continue this process until we reach the end if linked list.
Method 3 : (Floyd Algorithm)
Algorithm :
1) We will take two reference one is named as fast and other as slow .
2) Slow will be incremented by one(slow=slow.next) and fast will be incremented by
two(fast=fast.next.next) .
3) If slow becomes equal fast then it means there is a loop otherwise no loop is present .
4) Loop termination condition is when fast.next !=null and fast.next.next!=null .
Visualization of above algorithm :
1) Initially both slow and fast reference are at the head .
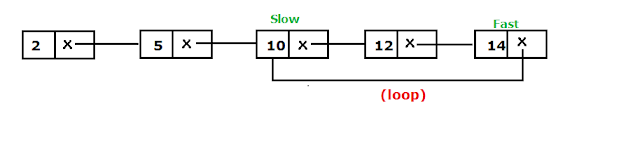
3) Now after incrementing again slow by one(slow=slow.next) and fast by two (fast=fast.next.next). Slow will reach to 10 and fast will reach 14 .
4) Increment slow again by one and fast by two. Both will reach to 12 . Hence proving that the there is a loop in linked list .
Function Implementation :
Please comment if you like the above post or if you find any mistake or have another better method of solving the above question .
Method 1 : ( Brute Force Method)
Brute Force Method is that start with first node and see whether there is any node whose next pointer is current node address . If there is a node with same address then that indicates that some other node is pointing to the the current node and showing there is loop int the linked list . Repeat this process until all the nodes are traversed or checked .
Method 2 : (Hashing )
1) Traverse the linked list nodes one by one and save address of the node in a table .
2) Check if the node address is there in hash table or not .
3) If it is already there in the hash table then that indicates that we are visiting the node which was already visited . This is possible only if the given linked list has a loop in it.
4) If the address of the node is not there in the hash table the insert that node address into the hash table .
5) Continue this process until we reach the end if linked list.
Method 3 : (Floyd Algorithm)
Algorithm :
1) We will take two reference one is named as fast and other as slow .
2) Slow will be incremented by one(slow=slow.next) and fast will be incremented by
two(fast=fast.next.next) .
3) If slow becomes equal fast then it means there is a loop otherwise no loop is present .
4) Loop termination condition is when fast.next !=null and fast.next.next!=null .
Visualization of above algorithm :
1) Initially both slow and fast reference are at the head .
2) After incrementing slow by one(slow=slow.next) and fast(fast=fast.next.next) by two.
3) Now after incrementing again slow by one(slow=slow.next) and fast by two (fast=fast.next.next). Slow will reach to 10 and fast will reach 14 .
4) Increment slow again by one and fast by two. Both will reach to 12 . Hence proving that the there is a loop in linked list .
Function Implementation :
public static void
findingloop(LinkedList list) {
int flag = 0;
Node
slow = list.root;
Node
fast = list.root;
int size;
// if linked
list is null and fast reference has reached to null
// then
terminate the loop
while (slow != null && fast
!= null && fast.next != null) {
slow
= slow.next;
fast
= fast.next.next;
// if slow is
equal to fast it mean loop is present and terminate
// the loop
if (slow == fast)
{
flag
= 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag == 1) {
System.out.println("loop
found");
}
else {
System.out.println("Loop not
found");
}
}
Please comment if you like the above post or if you find any mistake or have another better method of solving the above question .




No comments:
Post a Comment